Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) & what they have to do with IoT
AICPScyber-physical systeminternet of thingsThe world has already witnessed three industrial revolutions, each profoundly influencing the trajectory of global economic development and the quality of human life. And now, at the cusp of Industry 4.0, cyber-physical systems (CPS) stand as one of its paramount driving forces.
With the ever-growing computational capabilities, sensor technologies, and groundbreaking strides in artificial intelligence, we find ourselves on the brink of a complete reimagining of industries and societal dynamics. Today, the vistas for automation, optimization, and efficient management span various domains, encompassing everything from industrial sectors and healthcare to transportation and smart cities.
Let’s delve into the realms of CPS and IoT to contemplate the limitless possibilities these cutting-edge technologies will unveil.
What do Cyber-Physical Systems have inside?
Cyber-Physical Systems represent sophisticated engineering systems that facilitate the seamless interaction between virtual and physical domains, exemplified by scenarios where computer algorithms govern mechanical processes.
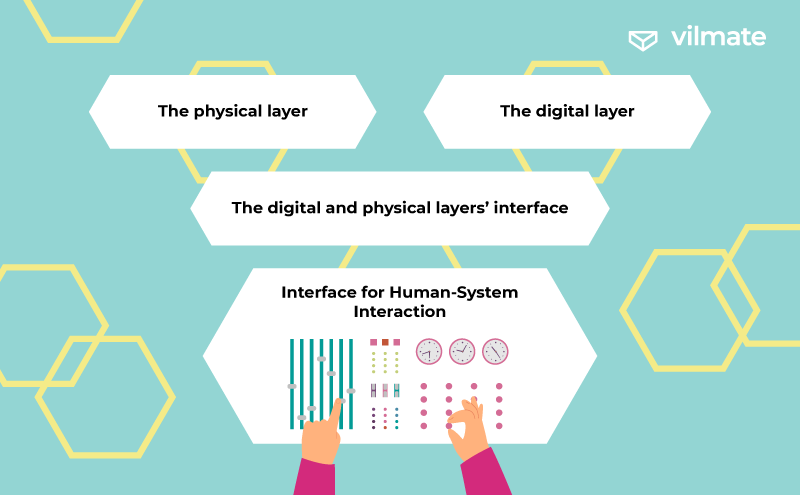
The essential constituents of a Cyber-Physical System are delineated as follows:
- The physical layer pertains to tangible real-world objects and entities.
- The digital layer encompasses computer algorithms, information processing protocols, and system data stored in the cloud.
- The digital and physical layers’ interface is realized by deploying sensors and control mechanisms.
- Interface for Human-System Interaction enables effective human engagement with the CPS.
While the term “Cyber-Physical Systems” came into prominence 15 years ago, people are beginning to fully embrace the vast potential these technologies offer only now. For instance, CPS is a focal research point in prominent laboratories like the University of California, Los Angeles. It is also being actively explored in engineering departments at Bosch and Toshiba.
Cyber-Physical Systems can be broadly categorized into two distinct groups: stationary and mobile systems, each with unique characteristics and applications.
- Stationary CPS Stationary CPS are integrated into specific systems and objects, such as manufacturing plants or smart homes. They are typically connected to local networks, which renders them less susceptible to cyber-attacks. Stationary cyber-physical systems collect data from physical components in a localized setting.
- Mobile CPS Mobile CPS operates spatially dynamically, exemplified by autonomous robots or self-driving vehicles. They can connect to various local, wireless, or cellular networks. Mobile cyber-physical systems are comparatively less secure; however, they can gather and transmit data from physical components to remote locations.
The growing interest in mobile cyber-physical systems can be attributed to the widespread adoption of smartphones. Smart devices possess robust computational resources and ample storage capacity, making them ideal hosts for CPS. Additionally, mobile devices are equipped with sensors, such as cameras, speakers, microphones, and GPS capabilities. Furthermore, smartphones support multiple communication protocols, including Bluetooth, Wi-Fi, and mobile networks.
The integration of smartphones has led to the emergence of critical cyber-physical systems that can perform real-time on-site analysis.
Undoubtedly, smartphones exert a profound influence on the progression of CPS. Nonetheless, the omnipotent force of Artificial Intelligence (AI) transcends these bounds.
AI is everywhere and CPS is no exception
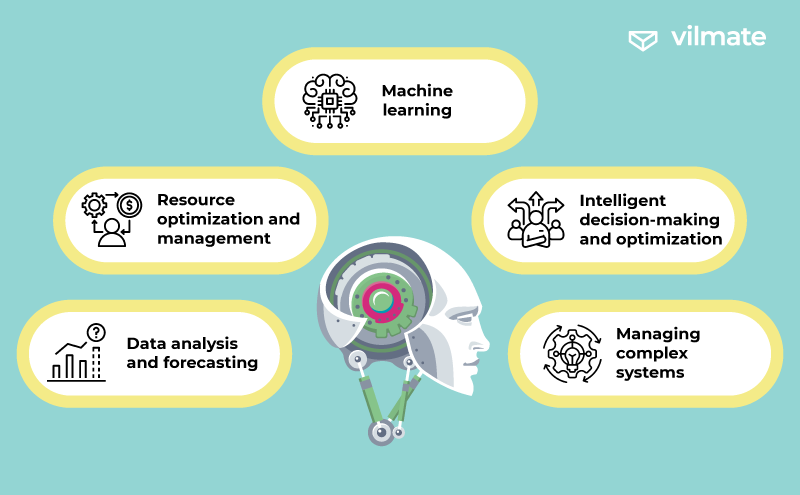
Artificial Intelligence plays a crucially vital role in advancing and enhancing Cyber-Physical Systems, empowering them to achieve newfound autonomy and reducing reliance on human intervention. Let’s delve into the key advantages of integrating AI into Cyber-Physical Systems.
1. Machine learning
At the core of Artificial Intelligence lies machine learning; computers learn from copious amounts of data through this process. This technology endows Cyber-Physical Systems with heightened intellect and the ability to adapt to novel situations based on accumulated experience.
2. Resource optimization and management
AI is harnessed to optimize CPS operations and efficiently manage resources. For instance, in industrial settings, AI can govern production processes to maximize efficiency while minimizing costs.
3. Data analysis and forecasting
Through the integration of Artificial Intelligence, CPS can meticulously analyze vast volumes of data collected from sensors and other sources. AI empowers CPS to forecast future events, optimize system performance, and proactively mitigate potential issues.
4. Intelligent decision-making and optimization
AI-equipped CPS are endowed with the capability to make intelligent decisions based on data and situational analysis. This responsive interaction enables automatic adaptation to environmental changes and facilitates the pursuit of optimal decisions to achieve predefined objectives.
5. Managing complex systems
Cyber-Physical Systems can be intricate, comprising numerous components and interactions. AI is the orchestrator, managing this intricacy by coordinating the workings of diverse system components, all geared towards attaining overarching goals.
Can CPS function without Artificial Intelligence? Yes, of course. CPS can operate based on algorithms and rules. However, AI empowers Cyber-Physical Systems to reach an entirely new level, becoming the revolutionary technology of Industry 4.0.
The concept of CPS is quite complex, so we must examine examples to understand the technology and its prospects fully.
A few examples of CPS for the story
For a clearer demonstration, let's examine examples that are familiar to many: autonomous vehicles and smart homes.
The most straightforward illustration of a Cyber-Physical System is the autonomous vehicle. Let’s leverage this example to elucidate the overarching concept of CPS and bring all the pieces together.
A Cyber-Physical System harmoniously amalgamates digital and physical components, enabling automatic control of the vehicle’s motion while minimizing the need for driver intervention. The pivotal constituents of a self-driving car and their functionalities are as follows:
- Sensors
- Central Controller
- Actuators
The linchpin of physical manipulation, actuators are tangible devices governed by the central controller’s determinations. These electronic control units proficiently manage acceleration, braking, steering, and other intricate vehicular systems.
As you can discern, an autonomous vehicle encapsulates all the quintessential components of a Cyber-Physical System. Let’s delve into their practical functioning and see them in action.
- Data Collection: Sensors in the autopilot-enabled car continuously gather data about the road conditions and surrounding objects.
- Data Processing: The collected data is sent to the central controller, which analyzes the information and makes informed decisions about how to proceed.
- Decision-Making: The central controller employs advanced algorithms and artificial intelligence to make optimal decisions regarding the car’s behavior on the road, including adjusting speed, changing lanes, braking, or executing other maneuvers.
- Actuator Control: Following the decision-making process, the central controller sends precise commands to the actuators to perform the necessary actions. For instance, if braking is required, the central controller will issue a command to activate the brakes.
- Vehicle Movement: The car dutifully follows the commands from the central controller, allowing it to navigate the road without direct intervention from the driver or with minimal input for system oversight.
While autopilot-enabled cars offer unparalleled convenience and have the potential to enhance road safety significantly, they also encounter various limitations and challenges. For instance, autopilot systems may not always flawlessly respond to unexpected road situations, such as construction work, unpredictable behavior of other drivers, or extreme weather conditions.
Nevertheless, given the rapid progress in artificial intelligence, it’s highly likely that these issues will be effectively addressed soon.
Another popular application of Cyber-Physical Systems is found in smart homes. A smart home is a stationary CPS that interconnects various physical components, such as Internet of Things (IoT) devices, sensors, actuators, computer systems, and software, to automate and enhance the living experience of its residents.
The following are the advantages that CPS offers for smart homes:
- Intelligence: Smart homes have intelligent capabilities due to embedded sensors and control systems. These features enable them to gather information about the surrounding environment and residents’ behaviors.
- Automation: Smart home systems are designed to respond automatically to specific events and conditions. For example, they can adjust the temperature, activate lighting, or engage security systems based on the current needs of the residents.
- Efficient Resource Utilization: Smart homes can optimize energy and resource usage by automatically regulating thermostats, turning off idle appliances, and optimizing irrigation systems.
- Security: Smart home security systems protect against unauthorized access and alert residents about hazardous situations, such as intrusions or fires.
- Interoperability: Smart homes integrate various devices and systems, including lighting, heating, cooling, security, and home appliances, enabling them to work cohesively and collaboratively.
Examples of smart devices that can be integrated into a smart home within the context of CPS include smart thermostats, smart lighting fixtures, smart smoke and carbon monoxide detectors, smart locks, smart video doorbells, as well as smart home assistants like Amazon Echo or Google Home.
Now that we have explored tangible examples of Cyber-Physical Systems let us delve deeper into the domains where they can be applied.
Primary application areas of CPS
We have already discussed how engineers apply CPS in the automotive industry. Additionally, we have explored how smart homes function as stationary cyber-physical systems. Taking a cue from smart homes, governments can also implement CPS to create smart cities. For instance, in Singapore, cyber-physical systems are being planned for traffic management and optimized urban mobility.
However, the potential of cyber-physical systems extends far beyond these domains.
1. Manufacture
Undoubtedly, CPS plays a pivotal role in advancing industries, which is why it’s considered a crucial component of Industry 4.0. Let’s delve further into cyber-physical systems’ possibilities in the industrial sector.
- Automation and robotics: CPS enable the automation of a myriad of manufacturing processes by integrating robots and intelligent machines. CPS leads to heightened productivity, improved product quality, and decreased risks for the workforce.
- Intelligent production lines: CPS facilitates the creation of flexible and adaptive production lines that can swiftly switch between various products and promptly respond to market demands.
- Equipment monitoring and diagnostics: CPS allows real-time equipment condition monitoring, predicting potential malfunctions or breakdowns. This proactive approach enables timely maintenance, reducing equipment downtime.
- Digital twins: CPS is harnessed to create and enhance digital twins of production processes. These virtual representations of physical systems facilitate the modeling and optimization of manufacturing operations.
- Integration with suppliers and customers: CPS streamlines manufacturing processes by seamlessly integrating with suppliers and customers, simplifying supply chain management and logistics.
- Energy efficiency and resource optimization: CPS empowers industries to optimize energy consumption and resource utilization, leading to cost savings and enhanced environmental sustainability.
Envision a future where the industrial sector becomes hyper-targeted. Companies will have the capability to produce goods tailored precisely to individual customers, effortlessly customizing products to cater to their unique needs. This exciting prospect is made attainable by the transformative potential of CPS.
2. Agriculture
Cyber-Physical Systems are indispensable in agriculture as they contribute significantly to process optimization, increased food production, and the promotion of healthier produce.
- Smart farming: CPS enables the optimization of vital resources in farming, such as water and fertilizers. By integrating sensors and monitoring systems, soil conditions can be accurately assessed, determining the precise need for irrigation and fertilization, ultimately leading to higher yields and reduced operational costs.
- Precision farming: CPS facilitate precision agriculture, wherein specific field sections are treated individually based on their unique potential and requirements. This approach effectively minimizes resource waste and mitigates the environmental impact of conventional farming practices.
- Innovative livestock management: CPS finds practical application in monitoring the health and behavior of animals, determining optimal feeding regimes, and ensuring comfortable living conditions for livestock.
- Autonomous farming technologies: CPS plays a crucial role in developing autonomous technologies for crop harvesting, soil cultivation, plant fertilization, and other agricultural tasks. By leveraging cyber-physical systems, labor efforts are significantly reduced, leading to increased production efficiency and enhanced operational outcomes.
- Smart irrigation and plant protection systems: CPS are employed to manage advanced irrigation systems and to monitor and control plant pests and diseases effectively. This approach reduces water consumption and minimizes the reliance on chemical pesticides, promoting sustainable agricultural practices.
CPS proves invaluable in agriculture, offering practical solutions to address the numerous challenges the industry faces today.
3. Healthcare
Cyber-Physical Systems hold tremendous potential for applications in medicine and healthcare:
- Smart medical devices: In medicine, smart medical devices such as insulin pumps, pacemakers, and implanted sensors are utilized for patient monitoring and automated therapeutic procedures.
- Telemedicine: CPS enables telemedicine consultations and remote patient monitoring, which proves particularly beneficial for individuals residing in remote areas or having limited access to medical services.
- Robotic surgery: CPS finds application in robotic surgery, facilitating complex manipulations and high-precision operations with minimal invasiveness.
- Smart medication systems: Equipped with sensors, smart medication systems can promptly alert patients about the need to take prescribed medicines and help track medication adherence.
- Assistance for the elderly: By utilizing sensors, cyber-physical systems can effectively monitor the health of elderly individuals, detect falls, and analyze behavior to identify potential risks.
- Robot assistants: CPS is on the cusp of revolutionizing healthcare by developing smart robots capable of providing care for seriously ill patients or assisting individuals with limited abilities.
Integrating cyber-physical systems in medicine enhances medical services, improves diagnostic and treatment efficacy, and elevates patients’ overall comfort and quality of life. Nevertheless, it’s paramount to ensure the security and confidentiality of data to safeguard patients’ health and personal information.
When considering cyber-physical systems within the medical context, one might question the differences between CPS and the Internet of Things (IoT). After all, both involve smart devices that monitor patients’ health, detect falls (e.g., Apple Watch), and provide medication reminders. To clarify this aspect, let us delve deeper into the distinctions between CPS and IoT.
CPS vs. IoT: Understanding the Difference
As we know, Cyber-Physical Systems are designed to facilitate the seamless interaction between the digital and physical realms, allowing for mutual influence. Conversely, the Internet of Things comprises diverse sensors and detectors, primarily focused on gathering information and exchanging data with other devices.
The operation of IoT doesn’t necessitate human intervention, in contrast to CPS, which can proactively respond to changes in external conditions, thereby optimizing their performance. However, the evolution of IoT has precipitated a remarkable advancement in the realm of CPS. Through integration with the Internet of Things, cyber-physical systems can further elevate the efficiency of automation processes. For instance, envision a robot on a production line responsible for assembling automobiles. Thanks to IoT, a person can remotely oversee the process or entrust the management to artificial intelligence.
To better understand the difference between IoT and CPS, let’s delve into the world of... vacuum cleaners!
- An IoT-enabled vacuum cleaner can gather external data, such as cleaning duration, covered area, battery level, operational status, etc. All this valuable information is collected and seamlessly transmitted to your application via Wi-Fi.
- As part of a CPS, a vacuum cleaner transforms into a responsive robot capable of actively adapting to real-time changes in its environment. For instance, it may come equipped with advanced sensors to detect obstacles, variations in floor surfaces, or dirtiness.
While this illustration may not encompass the entirety of CPS capabilities, it effectively underscores the distinctions from IoT.
Of course, the significance goes far beyond mere room cleaning convenience. We’ve looked at the practical possibilities of cyber-physical systems before, so now it’s time to consider how they will develop.
The blooming future of Cyber-Physical Systems
The future of Cyber-Physical Systems holds captivating prospects for various aspects of human life and industries. CPS will continue to evolve in the forthcoming years, introducing new innovations and advancements. We have already discussed the integration with Artificial Intelligence, which will drive significant technological progress.

Here are some other aspects of CPS' future:
- Wireless and decentralized Networks: The future CPS will encompass more sophisticated wireless communication networks, enabling devices to exchange data and interact swiftly. Decentralized networks will foster more flexible and reliable CPS operations.
- Autonomous and resilient systems: In the future, CPS will become increasingly independent and capable of making decisions without constant human intervention. They will possess self-learning capabilities and exhibit improved resilience to unforeseen situations and failures.
- Ubiquitous application in various industries: CPS will be integrated into an ever-expanding array of industries, such as transportation, healthcare, manufacturing, agriculture, energy, and more. This integration will optimize processes, enhance productivity, reduce costs, and improve service quality.
- Ethical and legal considerations: As CPS develops, new ethical and legal challenges will emerge concerning data privacy, accountability for autonomous system decisions, and security concerns. Discussions will be necessary to establish appropriate standards and regulations to ensure CPS’s safe and effective utilization.
- Global connectivity: CPS will play a pivotal role in creating the Internet of Everything, where all devices, systems, and people will be interconnected, exchanging data and collaborating harmoniously to enhance the quality of life and societal development.
According to research, by 2028, the CPS market capitalization is expected to reach $137,556 million. For comparison, in 2022, the market capitalization was $86,979.6 million. Overall, the future of cyber-physical systems promises to be captivating and revolutionary as these systems become an integral part of our daily lives, contributing to progress and advancements across various spheres of human endeavor.
Final Thoughts
Do androids dream of cyber-physical systems? They most certainly should. The future, wherein robots aid us in optimizing countless processes, is already around the corner. All that remains is to integrate the virtual and physical worlds seamlessly.
If you are searching for a company with a proven track record and expertise in crafting innovative solutions, look no further than Vilmate.
We provide top-notch Services and support in IT development, assisting businesses in implementing cutting-edge Technologies and solutions to achieve their strategic objectives. With a wealth of experience across diverse projects and clientele, Vilmate is an ideal partner for your enterprise.




