Whether you’re onboarding a client, fulfilling an order, or preparing a budget, you typically follow a process or a set of steps.
However, processes can become outdated over time. What may have worked in the past may not be the most efficient today.
So, how can you improve your processes?
This is where business process management (BPM) comes in — the practice of analyzing and improving existing processes to increase their efficiency.
BPM sounds straightforward enough, but dig deeper, and you’ll find tons of acronyms and complex terminology. Keeping track of them all can be difficult.
This article provides a glossary of common business process terminology with definitions and examples. We’ll also provide links to additional resources so you can learn more about each.
Click the links below to jump ahead:
- Automation
- Bottleneck
- Business Automation Tool
- Business Process
- Business Process Management (BPM)
- Business Process Analysis
- Business Process Automation
- Business Process Design
- Business Process Diagram
- Business Process Reengineering
- Business Process Transformation
- Business Rules
- Continuous Process Improvement
- Dashboard
- Digital Signature
- Document Workflow Management
- Low-Code/No-Code
- Operational Excellence
- Standard Operating Procedure (SOP)
- Process Flow Diagram
- Process Improvement
- Process Mapping
- Workflow
- Workflow Analysis
- Workflow Diagram
- Workflow Engine
- Workflow Management
- Workflow Model
1. Automation Definition
Automation is the use of technology to automate repetitive tasks and minimize human input. It can increase productivity, minimize errors, and lower operating costs.
94% of employees say they spend parts of their day on tedious and time-consuming tasks like manual data entry, document creation, and invoice management.
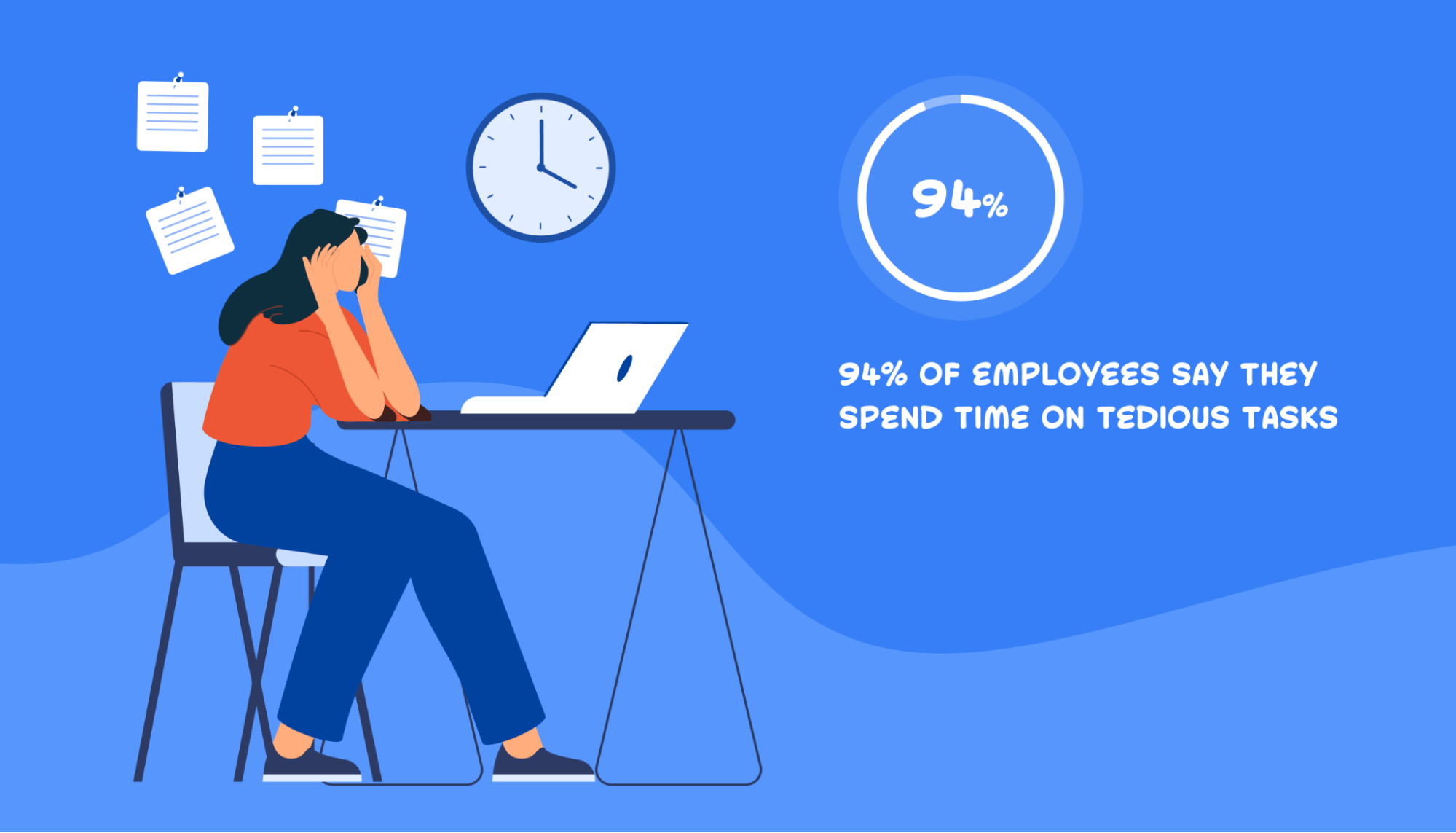
By automating repetitive processes, employees can spend less time on error-prone tasks and more time on strategic initiatives.
2. Bottleneck Definition
A bottleneck is a setback or obstacle that delays a process. It can increase turnaround times and processing costs.
Consider the contract approval process. If one person is in charge of approving contracts, projects might be delayed if they call in sick.
Common signs of bottlenecks include:
- Long wait times
- Continuous errors
- Backlogged work
- Unhappy staff
- Dissatisfied end users
These indicate that your processes aren’t as efficient as they should be. Learn how to identify bottlenecks in a process and how to address them.
3. Business Automation Tool Definition
A business automation tool helps companies automate their processes and reduce time spent on repetitive tasks.
Consider a task like document routing. Employees waste time when they chase down their managers to review and approve a document.
The right business automation tool can automate these steps and ensure that documents reach the right approvers.
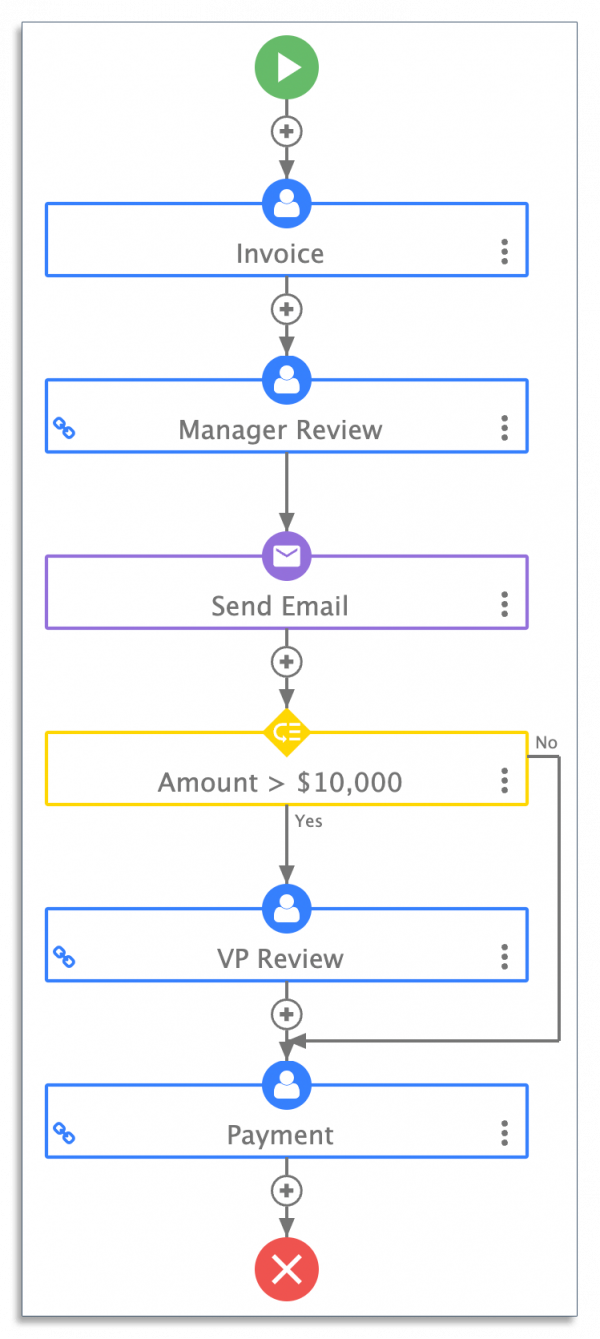
Learn more about business automation tools, including how they work, why you need them, and what the best automation platforms are.
4. Business Process Meaning
A business process is a series of steps you perform to achieve an objective. Examples include onboarding new hires, preparing goods for delivery, and approving contracts.
Nearly 50% of employees experience a lack of clarity in the workplace. Defining each step of a process can help employees understand their roles. Most importantly, it can also reveal opportunities for improvement.
Learn more about improving business processes, including why you should and how to get started.
5. Business Process Management (BPM) Definition
Business Process Management or BPM is the practice of analyzing an existing process, modeling improvements, and making changes to improve its efficiency.
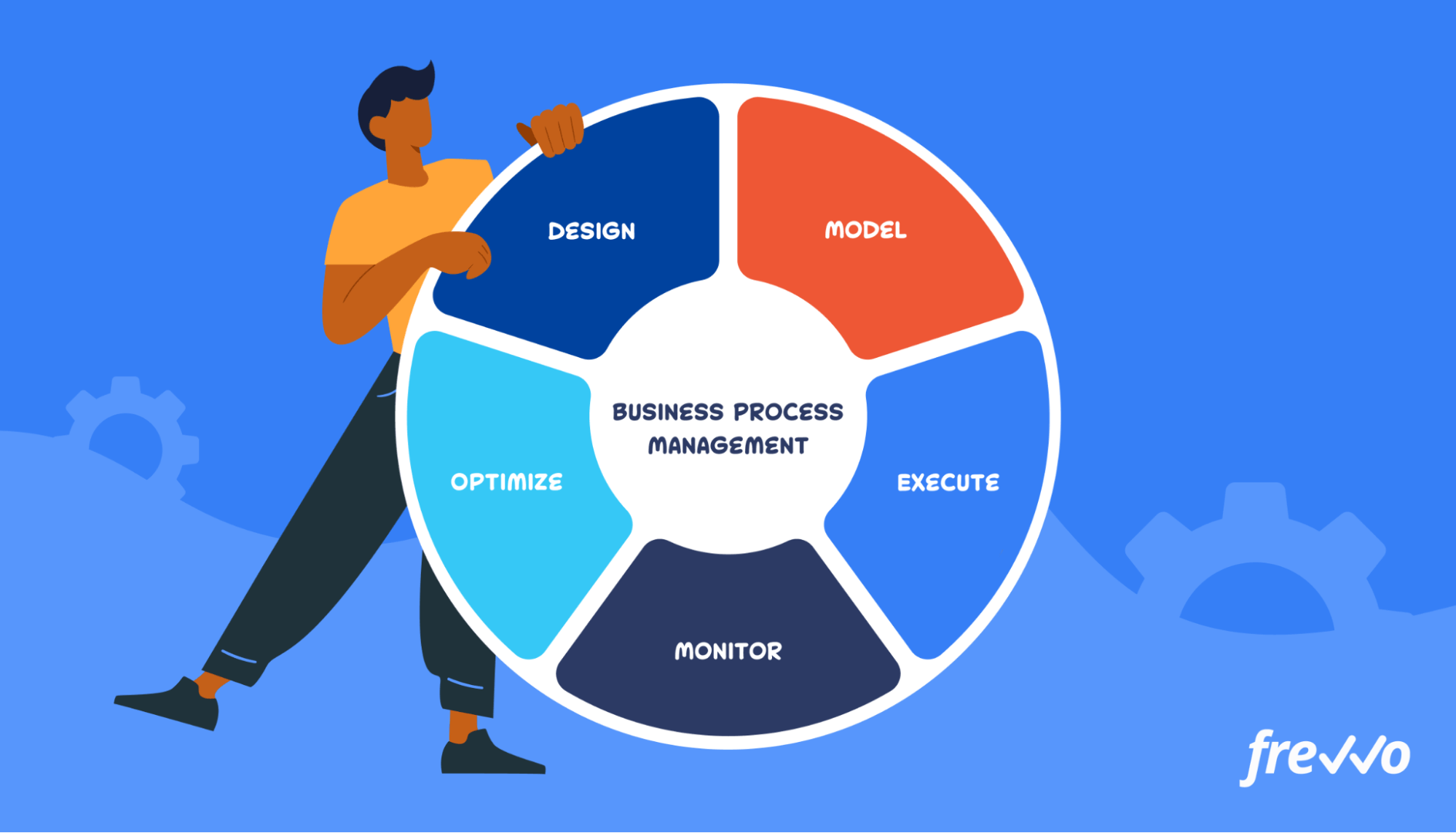
Processes can become outdated as your company changes. If you don’t carefully examine a process, there could be steps that employees are performing incorrectly.
When implemented correctly, BPM has a positive impact on your bottom line. 75% of organizations agree that BPM processes and technologies have helped them accomplish their goals.
Follow these BPM best practices to manage your processes more effectively.
6. Business Process Analysis Definition
Business process analysis is the practice of analyzing an existing process with the goal of identifying and fixing any inefficiencies.
Imagine that turnaround times for purchase orders are longer than usual. Conducting an in-depth analysis can help you identify which steps are causing delays. With these insights, you can plan and implement improvements.
Learn how to perform a business process analysis in six steps.
7. Business Process Automation Meaning
Business process automation is the use of technology to automate manual processes. It can be as simple as automating follow-ups or as complex as onboarding a new hire.
60% of organizations can automate at least 1/3 of their day-to-day work activities.
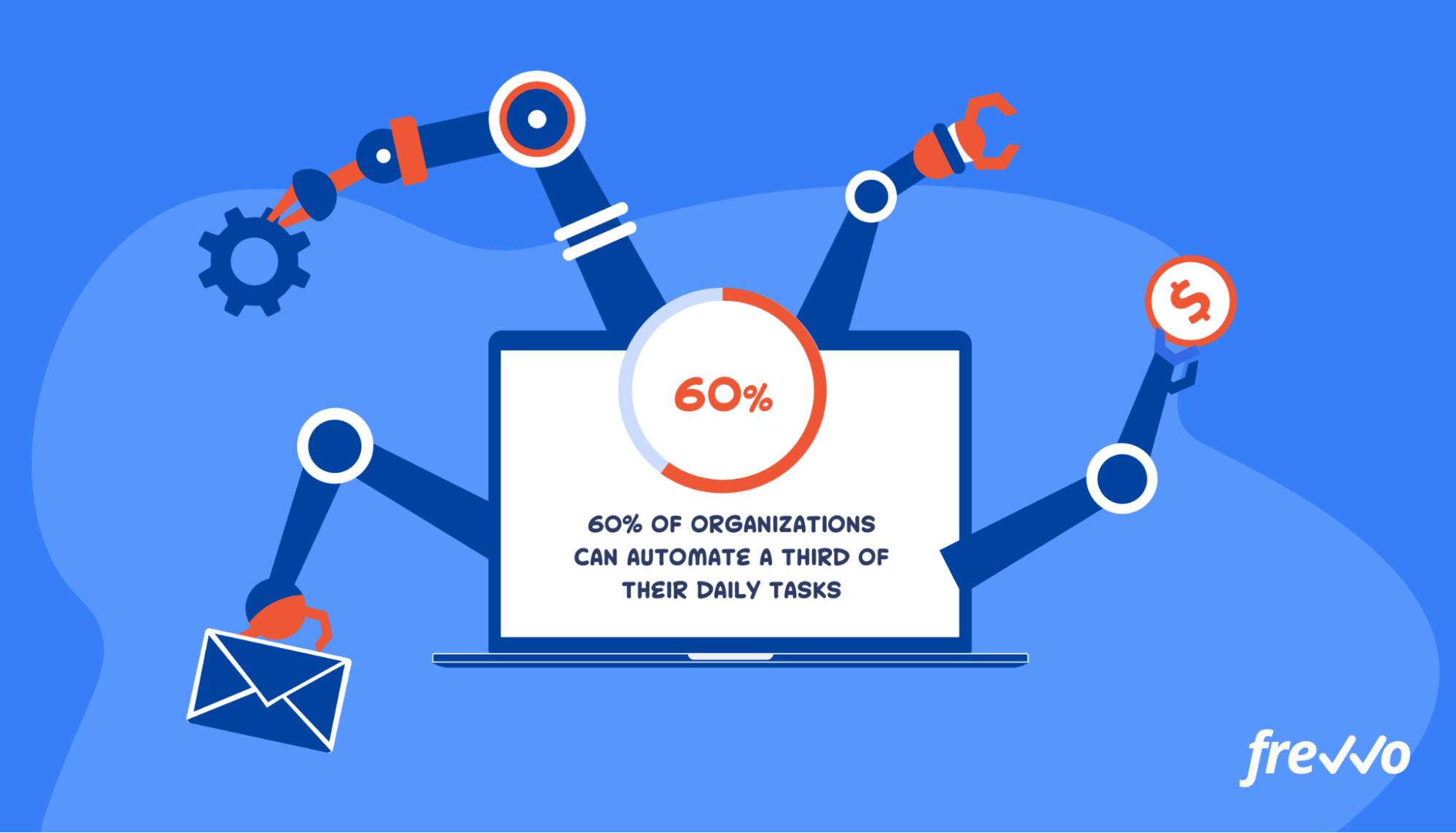
Using workflow automation software can help your company automate frequently-recurring tasks and improve overall efficiency.
Learn more in our comprehensive business process automation guide.
8. Business Process Design Definition
Business process design is the practice of creating or developing a new process from the ground up.
As a company scales, it can no longer take an ad-hoc approach to operations — it must design new processes to support growth.
Designing new processes will bring more structure to your organization and allow you to create repeatable processes that deliver consistent results.
Learn more in our ultimate guide to business process design, including why it’s important and the best way to design a process.
9. Business Process Diagram Definition
A business process diagram is a diagram that depicts each step of a process from start to finish. It uses standardized symbols like ovals, rectangles, and arrows to describe how work is completed.
Here’s an example of a business process diagram for purchase orders:
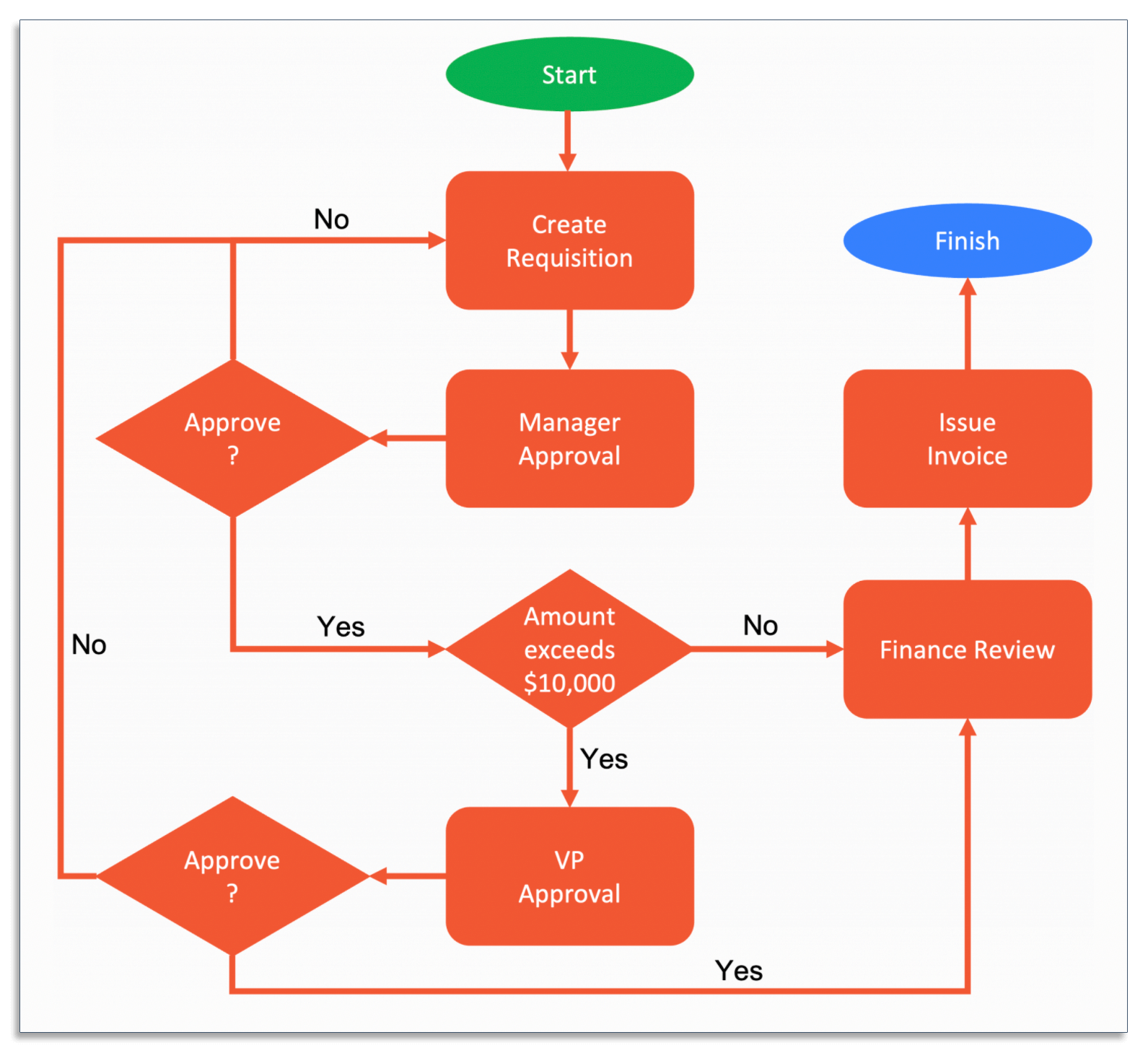
Creating a diagram gives you a top-level view of how a process works, allowing you to identify inefficiencies that may have been overlooked before.
Learn more about how to create a business process diagram and how to automate each step.
10. Business Process Reengineering Definition
Business process reengineering, not to be confused with business process design, is the practice of completely overhauling an existing process.
Making incremental changes is a common way to improve a process. But one downside is it can take a long time to start seeing results.
Sometimes it makes more sense to make radical changes, something that more companies are embracing. 40% of organizations are now focused on major process redesign projects.
Learn more about business process reengineering and the exact steps to follow to redesign your processes.
11. Business Process Transformation Definition
Business process transformation is the practice of changing aspects of a workflow to meet new business goals.
It typically involves using automation technologies to automate repetitive tasks and modernize manual processes. 65% of organizations view business transformation as a way to improve productivity and improve efficiency.
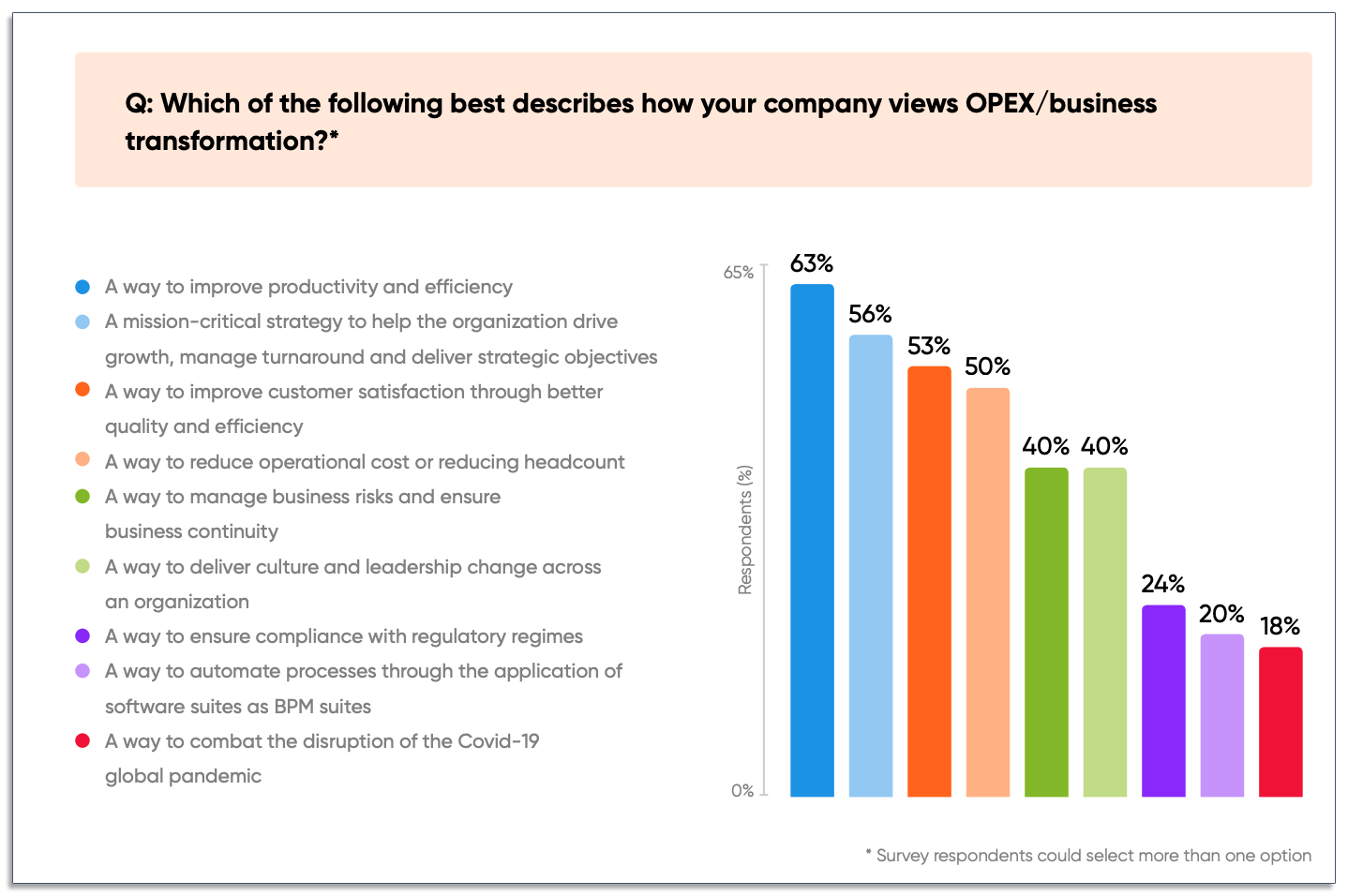
Learn more about business process transformation and see real examples of how companies are transforming their processes.
12. Business Rules Meaning
Business rules are a set of instructions that you apply to a process. They guide decision-making by establishing guidelines that employees must follow, which helps create more consistent outcomes.
Here’s an example of a business rule to perform calculations:
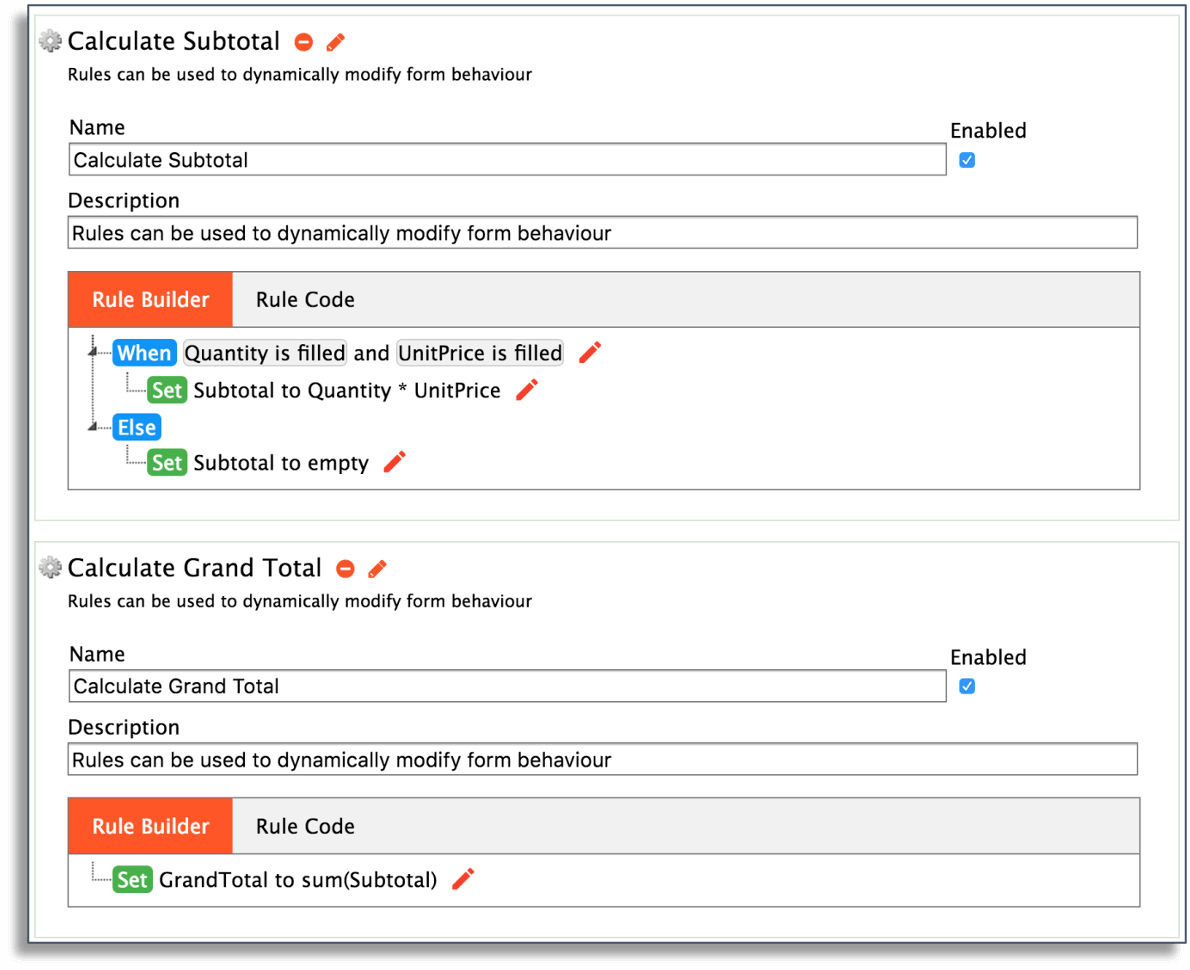
Common examples of business rules include:
- Conditionally routing documents
- Improving compliance with internal policies
- Validating data fields
- Performing calculations automatically
- Showing or hiding form sections
- Requiring signatures
See more examples of business rules and ways you can apply them across your organization to streamline operations.
13. Continuous Process Improvement Meaning
Continuous process improvement is an ongoing effort to improve existing processes through incremental changes. It originates from the Kaizen methodology, a Japanese term that translates to “change for the better.”
The most famous example is the use of Andon Cords in Toyota factories.
If an employee noticed a problem, they could halt production and offer suggestions. Small changes on the assembly line resulted in significant improvements over time.
Learn more about continuous process improvement and the methodologies you can implement to improve your processes.
14. Dashboard Definition
A dashboard is a graphical interface that lets you track and measure key performance indicators (KPIs) that are relevant to a process.
Here’s an example of a dashboard in frevvo:
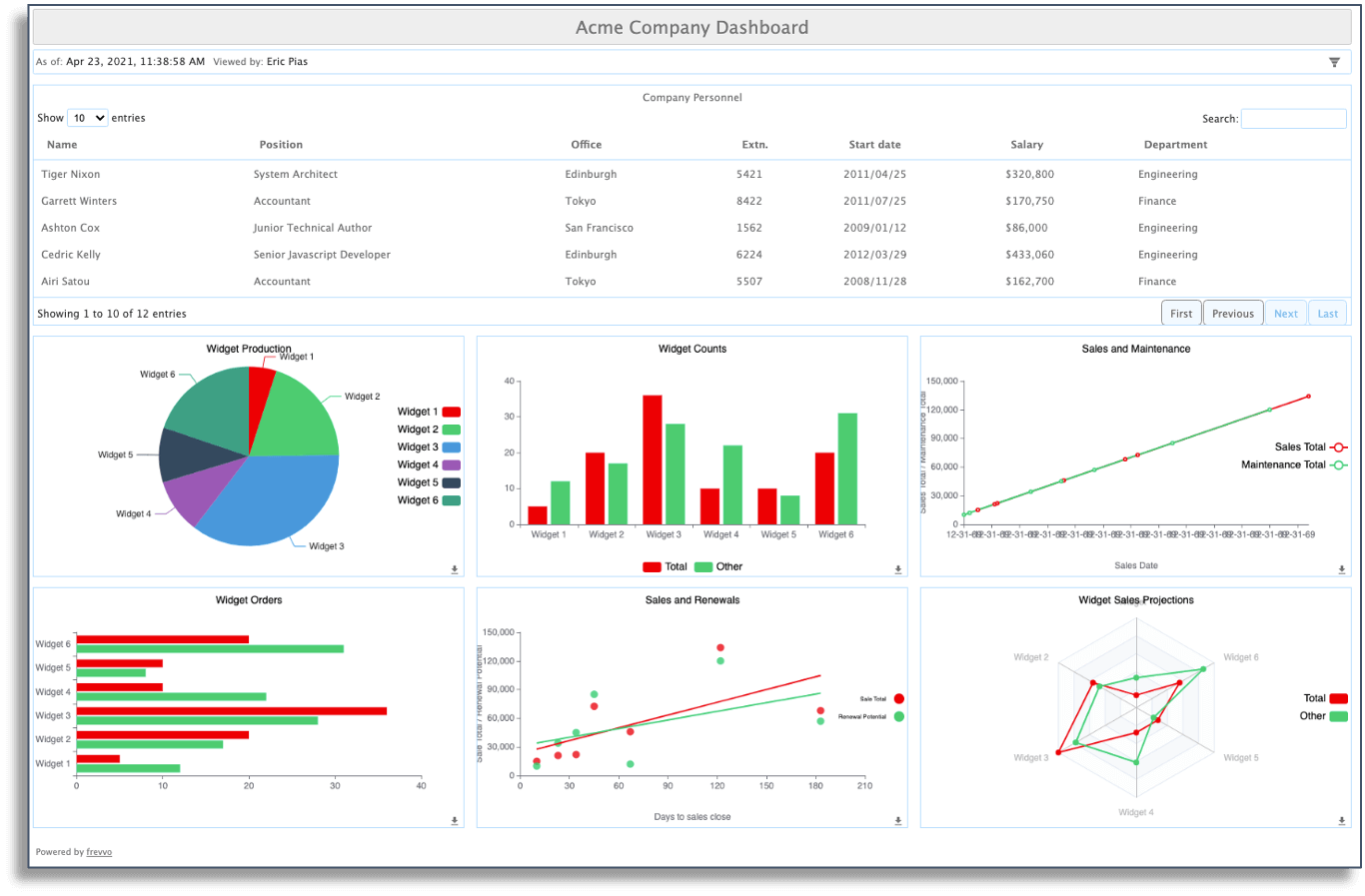
The dashboard displays metrics like submission activity, workflow durations, and more. These metrics provide valuable insights that you can use to improve your processes.
15. Digital Signature
Digital signatures are a type of electronic signature that use advanced encryption to verify and authenticate a signatory’s identity.
The Uniform Electronic Transactions Act (UETA) and United States Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce (ESIGN) Act have established certain requirements that must be met for an electronic signature to be valid.
Each party must show an intent to sign and agree to do business electronically. The system must use time-stamped audit trails and ensure that records are protected.
frevvo supports digital signatures, allowing you to collect legally binding signatures on documents like purchase orders, sales contracts, and more.
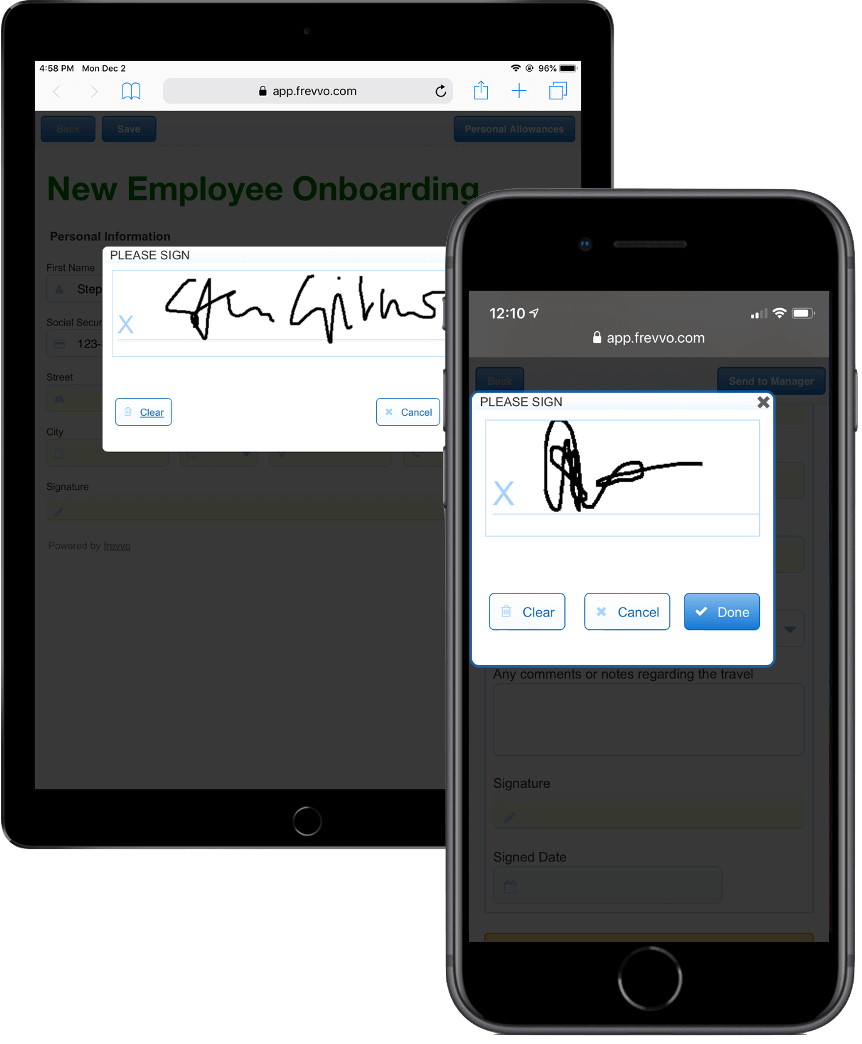
Learn how to create a digital signature workflow and how to ensure it complies with the requirements set by the UETA and ESIGN Act.
16. Document Workflow Management Definition
Document workflow management is a system that lets you create, store, sign, and retrieve documents related to a business process.
Most companies rely on countless documents to run their operations — purchase orders, contracts, invoices, expense claims, etc.
But managing these documents and the processes associated with them is challenging without the right system in place. 97% of organizations with manual or paper-based processes agree that the lack of technology affects their productivity.
Learn more about how you can streamline your workflows and digitize your document processes with a document workflow management system.
17. Low-Code/No-Code Meaning
A low-code or no-code platform allows users to build applications or processes using simple drag-and-drop tools. As the name suggests, these platforms require little to no coding experience.
Here’s an example of frevvo’s low-code workflow software:
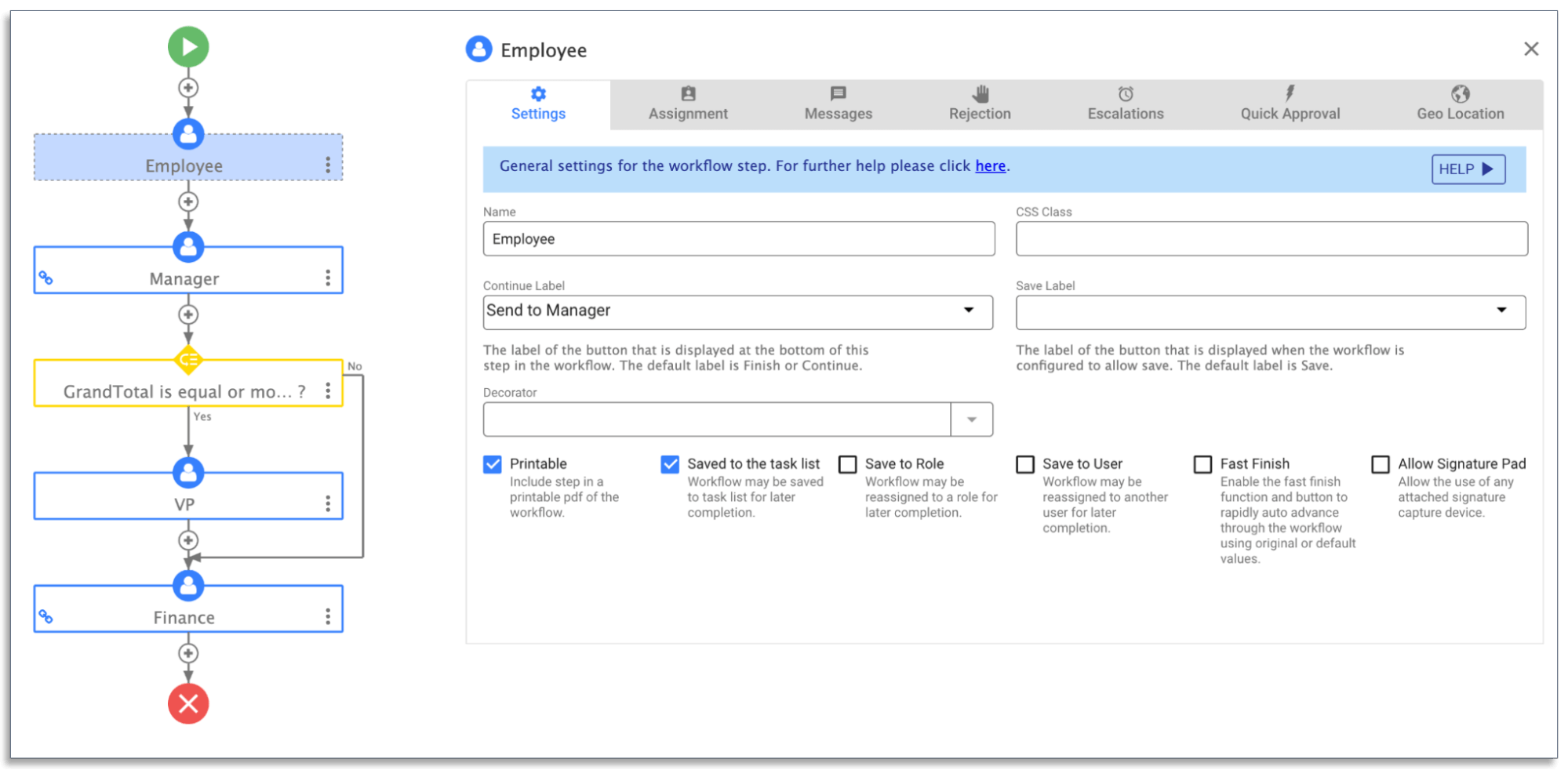
The software features a drag-and-drop form builder, point-and-click wizards, and visual builders that anyone can use to create automated workflows.
18. Operational Excellence Meaning
Operational excellence is the practice of continuously improving value streams across an organization. The goal is to deliver more value to end-users.
The assembly line is an example of a value stream. Manufacturers that optimize the production process can increase output, lower operating costs, and improve overall quality.
Learn more about how to achieve operational excellence and the methodologies you can adopt to optimize your value streams.
19. Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) Definition
A standard operating procedure (SOP) is a document that details the steps employees should follow when performing a task.
60% of employees find it hard to get the information they need to do their jobs. If processes aren’t clearly defined, employees may carry out a task in a way they shouldn’t.
Learn how to write an SOP and see a finished example.
20. Process Flow Diagram
A process flow diagram is a flowchart that uses symbols and notations to illustrate each step of a process.

Here’s a brief overview of what each symbol means:
- Ovals: Ovals represent the start and end points of a process.
- Rectangles: Rectangles describe a specific activity (e.g., an employee creates a purchase order).
- Diamonds: Diamonds indicate a decision (typically a yes or no question) in a workflow.
- Arrows: Arrows indicate the direction and next step of a workflow.
Learn how to create a process flow diagram and how to automate each step using workflow automation software.
21. Process Improvement Definition
Process improvement involves following a methodology to analyze a process, identify inefficiencies, implement new changes, and measure progress.
Common process improvement methodologies include:
- DMAIC: DMAIC stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. It provides a framework that facilitates improvements.
- Six Sigma: Six Sigma is a method that helps companies measure and eliminate defects in a process.
- Lean manufacturing: Lean manufacturing is based on the methodology of maximizing productivity and minimizing waste.
- PDCA: PDCA stands for Plan, Do, Check, and Act. It takes an iterative approach to improving a process.
- Agile: Agile is a methodology commonly used in software development to build and develop software in stages.
Follow these process improvement steps to learn how to identify problems and create solutions.
22. Process Mapping Definition
Process mapping is the practice of laying out a process from start to finish. It outlines who is responsible for carrying out tasks in each step.
You can create a process map by hand or use process mapping software. The latter will allow you to use automation across your processes.
Here’s an example of a process for approving expense claims:
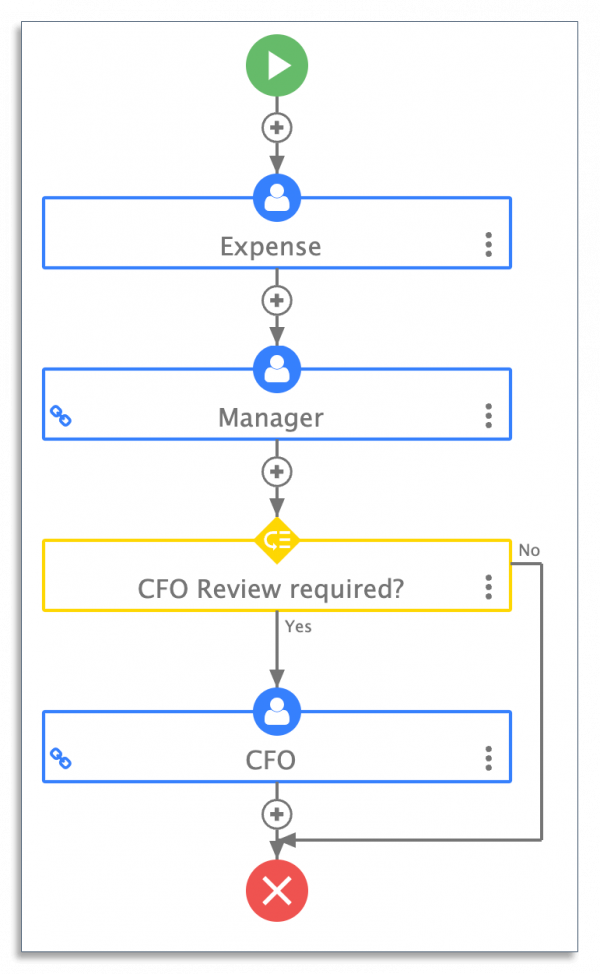
Learn more about process mapping and best practices that you should follow.
23. Workflow Meaning
A workflow is a series of repeatable steps that you follow when carrying out everyday activities to accomplish a specific objective.
Well-defined workflows are important because they ensure that employees follow each step in a process to the same standards, whether they’re preparing sales contracts, managing deliveries, or resolving complaints.
Learn more about workflows, including why you should create them and how to choose a workflow automation tool.
24. Workflow Analysis Meaning
Workflow analysis is the practice of analyzing each step of a workflow and finding ways to improve its efficiency.
Workflows help your company standardize its processes, but they can become inefficient as your operations scale. Letting these inefficiencies continue will have a direct impact on your bottom line.
Learn how to perform a workflow analysis so that you can identify and address any bottlenecks in your processes.
25. Workflow Diagram Definition
A workflow diagram is a graphic that depicts a workflow from start to finish. It uses standardized symbols to describe what happens at each step and who is responsible for them.
The easiest way to create a workflow is to simply write down the steps. But depending on how complex a workflow is, you may want to create a diagram instead.
Here’s an example of a workflow diagram for purchase orders:

Learn more about how to create a workflow diagram and how you can apply them across your organization.
26. Workflow Engine Definition
A workflow engine is software that lets you create and automate your workflows. It features a script that automatically “pushes” a task forward.
74% of business leaders and employees say that parts of their jobs can be automated. A workflow engine can help you automate repetitive tasks and free up employees to focus on more productive work.
Learn more about how a workflow engine works.
27. Workflow Management Definition
Workflow management involves managing, organizing, and optimizing workflows. The goal is to maximize their output without compromising on quality.
29% of organizations mostly or always complete projects on time. By better managing your workflows, you can help your team become more productive and meet their deadlines.
However, a company can have dozens, or even hundreds, of workflows. Managing them isn’t feasible without a workflow management system — a tool that lets you create, manage, and organize your workflows from one central location.
Learn about the essential features to look for when choosing a workflow management system.
28. Workflow Model Meaning
A workflow model provides a graphic overview of a workflow. It uses standardized symbols to illustrate each step from start to finish.
Workflow models typically include the following:
- Stakeholders: Stakeholders are the people who are directly involved in a workflow.
- Activities: Activities are the specific tasks that stakeholders are responsible for.
- Conditions: Conditions are rules that determine the next step in a workflow.
- Results: Results are the desired outcomes after completing each step.
Learn how to create a workflow model and how to optimize yours.
Conclusion
There you have it — a complete guide to business process terminology with examples and resources to help you better understand many of the terms that encompass this subject.
If you’re looking for a solution to automate and optimize your processes, then try a free 30-day trial today of frevvo’s workflow automation platform.

